Abstract
Introduction
The prognostic value of minimal residual disease (MRD) in mantle cell lymphomas (MCL) has been reported in several clinical trials mainly in younger patients eligible for autologous transplantation and allows preemptive treatment of relapse. In elderly patients, the MCL R2 Elderly trial evaluated the benefit of a maintenance treatment combining rituximab plus lenalidomide (R2) compared to rituximab alone (R) in patients responding to the randomized induction treatment, either the reference treatment R-CHOP or alternate RCHOP/R-HAD regimen. The clinical results of the trial will be reported during the present ASH-2021 meeting. A secondary objective of the MCL R2 Elderly trial was to assess the ability of the experimental regimen to eradicate MRD, or the ability of the maintenance regimen to erase the poor prognostic value of MRD (+) at the end of induction treatment (EOI) or during maintenance.
Methods
Samples were collected at diagnosis, midterm, EOI and every 6 months during the 2 years maintenance period. Prospective quantitative MRD assessment on peripheral blood (PB) or bone marrow (BM) samples was performed in national reference laboratories in France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain and Portugal (All members of Euro-MRD network), using the standardized gold standard real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) of clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain VDJ junction (IGH) or IGH-BCL1 rearrangement. Samples with QPCR data below the quantitative range (BQR) were considered positive when 2 or 3 replicates were positive. Assay sensitivity ranged from 10 -4 to 10 -5. Depending of time point, MRD status was assigned from PB result alone or from both PB and BM. In the later case, MRD was judged (+) if at least one sample, PB or BM, was (+) by QPCR.
Results:
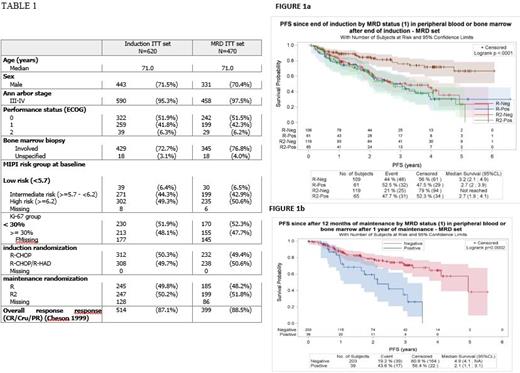
Tumoral marker was identified and MRD results were generated in 470 out of 532 tested patients (88% informativity). The analyses at 2 time-points are reported here: MRD at EOI in 401 patients who completed the induction treatment (R-CHOP n=192; R-CHOP/R-HAD, n=209) and MRD after one year under maintenance in 242 randomized patients (R n=114; R2 n=128). Clinical characteristics of the analyzed patients did not differ from the entire clinical cohort (Table 1). At the EOI, 157/401 (39%) patients were MRD(+), with no differences according to the induction regimen (81/192 [42.2%] in R-CHOP arm vs 76/209 [36.3%] in R-CHOP/R-HAD arm, p=0.23). With a median FU of 2.4 yrs from EOI, MRD(+) at EOI was significantly associated with a shorter median PFS (2.7yrs vs 4.7yrs, HR 1.78 [1.3-2.4] p=0.0002). However, the MRD status did not have the same impact in both maintenance arms (interaction test p=0.02). In the R arm, the 2 yr PFS was 64.8% and 61.7% for MRD(-) and MRD(+) patients, respectively (NS). In contrast, in the R2 arm, MRD did have a prognostic value: 84.3% vs 61.6% 2yr PFS for MRD(-) vs. MRD(+) patients, respectively (HR : 3 [1.78-5.1] p<0.0001) (Figure 1a), even when adjusted to MIPI. When only BM results were taken into account (n=320) HR increases (4 [2.2-7.3] p<0.0001).
MRD was analyzed both at EOI and after 1 year maintenance in 231 patients. In 191 patients (82.7%), the MRD status was identical at both time-points (35 (+)/(+) and 156 (-)/(-)). Only 3 patients converted from MRD (-) to MRD (+), 2 in the R and 1 in the R2 arm. MRD (+) to (-) conversion was observed in 16 (14.5%) and 21 (17.4%) patients in the R and R2 arms respectively (NS).
MRD status after one year of maintenance was obtained in 242 patients (203 MRD(-), 39 MRD (+)). MRD remained significantly associated with PFS, with a median PFS of 2.1 years and 4.9 years for MRD (+) and MRD (-) patients, respectively (HR 2.8 [1.6-5) p=0.0002) (figure 1b), with no interaction of maintenance arm.
Conclusion:
MRD assessment using standardized Euro-MRD QPCR demonstrated that the MRD status at EOI is of high prognostic value for PFS in elderly patients, but the observed effect is mainly due to the benefit provided by the R2 maintenance to the patients that are MRD(-) after induction. Whether undetectable MRD in these patients corresponds to very low disease levels (MRD<10-5), that can be immunologically controlled by the addition of lenalidomide to R, remains to be determined. A longer follow-up is needed to assess patient's outcome after the end of maintenance. Finally, our results show that patients MRD positive under maintenance, are at high risk of relapse, irrespective of treatment arm.
Delfau: AMGEN: Honoraria; GILEAD: Honoraria; MUNDIPHARMA: Honoraria; ROCHE: Honoraria, Research Funding; CELGENE: Research Funding. Gomes Da Silva: Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Klapper: Amgen: Research Funding; Regeneron: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding. Feugier: ROCHE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Meeting travel funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel funding. Safar: roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Casasnovas: Janssen: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Research Funding; TAKEDA: Consultancy, Research Funding; ROCHE: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy. Dreyling: Amgen: Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Genmab: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Research Funding; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Ribrag: Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Epizyme: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Infinity Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Nanostring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; PharmaMar: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Argen-X: Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal